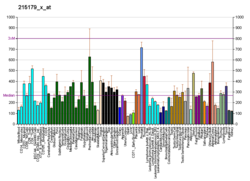
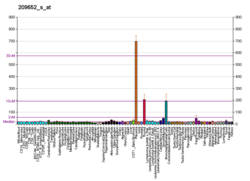
Placental growth factor (PlGF) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PGF gene.[5][6]
Placental growth factor (PGF) is a member of the VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) sub-family - a key molecule in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis, in particular during embryogenesis. The main source of PGF during pregnancy is the placental trophoblast. PGF is also expressed in many other tissues, including the villous trophoblast.[7]
The placental growth factor (PGF) gene is a protein-coding gene and a member of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family. The PGF gene is expressed only in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVE) and the placenta. PGF is ultimately associated with angiogenesis. Specifically, PGF plays a role in trophoblast growth and differentiation. Trophoblast cells, specifically extravillous trophoblast cells, are responsible for invading the uterine wall and the maternal spiral arteries. The extravillous trophoblast cells produce a blood vessel of larger diameter for the developing fetus that is independent of maternal vasoconstriction. This is essential for increased blood flow and reduced resistance.[8] Proper development of blood vessels in the placenta is crucial for the higher blood requirement of the fetus later in pregnancy. Under normal physiologic conditions, PGF is also expressed at a low level in other organs including the heart, lung, thyroid, and skeletal muscle.
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000119630 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000004791 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PGF placental growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein".
- ^ Maglione D, Guerriero V, Viglietto G, Ferraro MG, Aprelikova O, Alitalo K, Del Vecchio S, Lei KJ, Chou JY, Persico MG (April 1993). "Two alternative mRNAs coding for the angiogenic factor, placenta growth factor (PlGF), are transcribed from a single gene of chromosome 14". Oncogene. 8 (4): 925–31. PMID 7681160.
- ^ Khalil A, Muttukrishna S, Harrington K, Jauniaux E (July 2008). Lumbiganon P (ed.). "Effect of antihypertensive therapy with alpha methyldopa on levels of angiogenic factors in pregnancies with hypertensive disorders". PLOS ONE. 3 (7): e2766. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.2766K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002766. PMC 2447877. PMID 18648513.
- ^ Carlson, Bruce (2009). Human Embryology and Developmental Biology. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-323-05385-3.