| Plasmodium knowlesi | |
|---|---|
| |
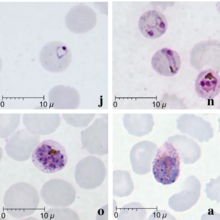
| Giemsa-stained smears of Plasmodium knowlesi infecting human red blood cells | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Apicomplexa |
| Class: | Aconoidasida |
| Order: | Haemospororida |
| Family: | Plasmodiidae |
| Genus: | Plasmodium |
| Species: | P. knowlesi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Plasmodium knowlesi Sinton and Mulligan 1932
| |
Plasmodium knowlesi is a parasite that causes malaria in humans and other primates. It is found throughout Southeast Asia, and is the most common cause of human malaria in Malaysia. Like other Plasmodium species, P. knowlesi has a life cycle that requires infection of both a mosquito and a warm-blooded host. While the natural warm-blooded hosts of P. knowlesi are likely various Old World monkeys, humans can be infected by P. knowlesi if they are fed upon by infected mosquitoes. P. knowlesi is a eukaryote in the phylum Apicomplexa, genus Plasmodium, and subgenus Plasmodium. It is most closely related to the human parasite Plasmodium vivax as well as other Plasmodium species that infect non-human primates.
Humans infected with P. knowlesi can develop uncomplicated or severe malaria similar to that caused by Plasmodium falciparum. Diagnosis of P. knowlesi infection is challenging as P. knowlesi very closely resembles other species that infect humans. Treatment is similar to other types of malaria, with chloroquine or artemisinin combination therapy typically recommended. P. knowlesi malaria is an emerging disease previously thought to be rare in humans, but increasingly recognized as a major health burden in Southeast Asia.
P. knowlesi was first described as a distinct species and as a potential cause of human malaria in 1932. It was briefly used in the early 20th century to cause fever as a treatment for neurosyphilis. In the mid-20th century, P. knowlesi became popular as a tool for studying Plasmodium biology and was used for basic research, vaccine research, and drug development. P. knowlesi is still used as a laboratory model for malaria, as it readily infects the model primate the rhesus macaque, and can be grown in cell culture in human or macaque blood.