| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1,7)-Polyoxepan-2-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Poly(hexano-6-lactone) | |
| Other names
2-Oxepanone homopolymer
6-Caprolactone polymer | |
| Identifiers | |
| Abbreviations | PCL |
| ChemSpider |
|
| Properties | |
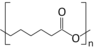
| (C6H10O2)n | |
| Density | 1.145 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 60 °C (140 °F) |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.05 W/(m K) @25°C[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a synthetic, semi-crystalline, biodegradable polyester with a melting point of about 60 °C and a glass transition temperature of about −60 °C.[2][3] The most common use of polycaprolactone is in the production of speciality polyurethanes. Polycaprolactones impart good resistance to water, oil, solvent and chlorine to the polyurethane produced.
This polymer is often used as an additive for resins to improve their processing characteristics and their end use properties (e.g., impact resistance). Being compatible with a range of other materials, PCL can be mixed with starch to lower its cost and increase biodegradability or it can be added as a polymeric plasticizer to polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Polycaprolactone is also used for splinting, modeling, and as a feedstock for prototyping systems such as fused filament fabrication 3D printers.
- ^ Sharma, Adit; Kopylov, Alexey; Zadorozhnyy, Mikhail; Stepashkin, Andrei; Kudelkina, Vera; Wang, Jun-Qiang; Ketov, Sergey; Churyukanova, Margarita; Louzguine-Luzgin, Dmitri; Sarac, Baran; Eckert, Jürgen; Kaloshkin, Sergey; Zadorozhnyy, Vladislav; Kato, Hidemi (2020). "Mg-Based Metallic Glass-Polymer Composites: Investigation of Structure, Thermal Properties, and Biocompatibility". Metals. 10 (7): 867. doi:10.3390/met10070867.
- ^ Kumbar, Sangamesh; Laurencin, Cato T.; Deng, Meng (2014). Natural and synthetic biomedical polymers (1st ed.). Burlington, MA: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-12-396983-5.
- ^ Narayan, Roger J. (2019), "Preface", Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering, Elsevier, pp. xxxv–xxxvi, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-804829-0.05001-x, ISBN 978-0-12-805144-3, retrieved 2023-11-01