 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sodium salt: Kayexalate, Kionex, Resonium A Calcium salt: Calcium Resonium, Sorbisterit, Resikali Potassium and sodium salt: Tolevamer |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682108 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, retention enema |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | None |
| Metabolism | None |
| Excretion | Faeces (100%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
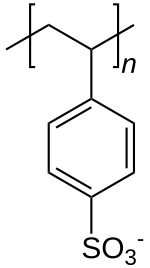
| Formula | [C8H7SO3−] n |
| | |
Polystyrene sulfonates are a group of medications used to treat high blood potassium.[1] Effects generally take hours to days.[1] They are also used to remove potassium, calcium, and sodium from solutions in technical applications.
Common side effects include loss of appetite, gastrointestinal upset, constipation, and low blood calcium.[1] These polymers are derived from polystyrene by the addition of sulfonate functional groups.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958.[1]
A polystyrene sulfonate was developed in the 2000s to treat Clostridioides difficile associated diarrhea under the name Tolevamer,[2] but it was never marketed.
- ^ a b c d "Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- ^ Hinkson PL, Dinardo C, DeCiero D, Klinger JD, Barker RH (June 2008). "Tolevamer, an anionic polymer, neutralizes toxins produced by the BI/027 strains of Clostridium difficile". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 52 (6): 2190–2195. doi:10.1128/AAC.00041-08. PMC 2415796. PMID 18391047.