| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
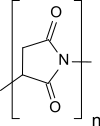
| IUPAC name
Poly(2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-1,3-diyl)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| (C4H3NO2)n | |
| Molar mass | 97.07 g·mole−1 |
| Appearance | solid |
* insoluble in water[1]
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Polysuccinimide (PSI), also known as polyanhydroaspartic acid or polyaspartimide, is formed during the thermal polycondensation of aspartic acid and is the simplest polyimide.[5] Polysuccinimide is insoluble in water, but soluble in some aprotic dipolar solvents. Its reactive nature makes polysuccinimide a versatile starting material for functional polymers made from renewable resources.[5]
The name is derived from the salt of succinic acid, the structurally related succinate.
- ^ E. Jalalvandi, A. Shavandi (2018), "Polysuccinimide and its derivatives: Degradable and water soluble polymers (review)", Eur. Polym. J., vol. 109, pp. 43–54, doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.08.056, S2CID 106107591
- ^ T. Klein, R.-J. Moritz, R. Graupner (2016), Ullmann's Polymers and Plastics, Products and Processes, Volume 1, Part 2: Organic Polymers, Polyaspartates and Polysuccinimide, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, pp. 742–743, ISBN 978-3-527-33823-8
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ M. Tomida, T. Nakato, M. Kuramochi, M. Shibata, S. Matsunami, T. Kakuchi (1996), "Novel method of synthesizig poly(succinimide) and its copolymeric derivatives by acid-catalysed polycondensation of L-aspartic acid", Polymer, vol. 37, no. 16, pp. 4435–4437, doi:10.1016/0032-3861(96)00267-4
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Baypure® General Product Information (PDF) Lanxess AG
- ^ a b Adelnia, Hossein; Tran, Huong D.N.; Little, Peter J.; Blakey, Idriss; Ta, Hang T. (2021-06-14). "Poly(aspartic acid) in Biomedical Applications: From Polymerization, Modification, Properties, Degradation, and Biocompatibility to Applications". ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering. 7 (6): 2083–2105. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c00150. hdl:10072/404497. PMID 33797239. S2CID 232761877.