The North America Portal
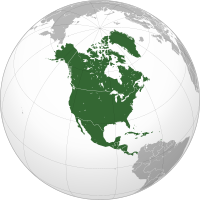
North America is a continent in the Northern and Western Hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes the Bahamas, Bermuda, Canada, the Caribbean, Central America, Clipperton Island, Greenland, Mexico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.
North America covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 square miles), representing approximately 16.5% of the Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. As of 2021[update], North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography, the terms "North America" and "North American" can refer to Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Greenland or, alternatively, Canada, Greenland and the US (Mexico being classified as part of Latin America) or simply Canada and the US (Greenland being classified as either Arctic or European (due to its political status as a part of Denmark) and Mexico classified as Latin American).
It is unknown with certainty how and when first human populations first reached North America. People were known to live in the Americas at least 20,000 years ago, but various evidence points to possibly earlier dates. The Paleo-Indian period in North America followed the Last Glacial Period, and lasted until about 10,000 years ago when the Archaic period began. The classic stage followed the Archaic period, and lasted from approximately the 6th to 13th centuries. Beginning in 1000 AD, the Norse were the first Europeans to begin exploring and ultimately colonizing areas of North America.
In 1492, the exploratory voyages of Christopher Columbus led to a transatlantic exchange, including migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery and the early modern period. Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples, enslaved Africans, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and descendants of these respective groups. (Full article...)
The Colorado River (Spanish: Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The 1,450-mile-long (2,330 km) river, the 5th longest in the United States, drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. states and two Mexican states. The name Colorado derives from the Spanish language for "colored reddish" due to its heavy silt load. Starting in the central Rocky Mountains of Colorado, it flows generally southwest across the Colorado Plateau and through the Grand Canyon before reaching Lake Mead on the Arizona–Nevada border, where it turns south toward the international border. After entering Mexico, the Colorado approaches the mostly dry Colorado River Delta at the tip of the Gulf of California between Baja California and Sonora.
Known for its dramatic canyons, whitewater rapids, and eleven U.S. National Parks, the Colorado River and its tributaries are a vital source of water for 40 million people. An extensive system of dams, reservoirs, and aqueducts divert almost its entire flow for agricultural irrigation and urban water supply. Its large flow and steep gradient are used to generate hydroelectricity, meeting peaking power demands in much of the Intermountain West. Intensive water consumption has dried up the lower 100 miles (160 km) of the river, which has rarely reached the sea since the 1960s. (Full article...)

Solomon Porcius Sharp (August 22, 1787 – November 7, 1825) was an American lawyer and politician, serving as attorney general of Kentucky and a member of the United States Congress and the Kentucky General Assembly. His murder by Jereboam O. Beauchamp in 1825 is referred to as the Beauchamp–Sharp Tragedy or "The Kentucky Tragedy."
Sharp began his political career representing Warren County in the Kentucky House of Representatives. He briefly served in the War of 1812, then returned to Kentucky and was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1813. He was re-elected to a second term, though his support of a controversial bill regarding legislator salaries cost him his seat in 1816. Allied with Kentucky's Debt Relief Party, he returned to the Kentucky House in 1817; in 1821, he accepted Governor John Adair's appointment to the post of Attorney General of Kentucky. Adair's successor, Joseph Desha, re-appointed him to this position. In 1825, Sharp resigned as attorney general to return to the Kentucky House. (Full article...)

The October 2008 Central America floods were caused by a series of low-pressure areas including Tropical Depression Sixteen, a short-lived tropical cyclone in the 2008 Atlantic hurricane season that made landfall in Honduras. Heavy rainfall began in early October 2008 while a tropical wave passed through the region. On October 14, Tropical Depression Sixteen formed just off the northeast coast of Honduras, and at the same time a low-pressure system was on the Pacific coast. Both systems increased rainfall across the region, although the depression dropped heavy rainfall close to its center when it moved ashore on October 15. Although Tropical Depression Sixteen quickly dissipated over land, its remnants persisted for several days. Another low-pressure area interacted with a cold front on October 21, adding to the rainfall in the region.
Heavy rainfall extended from Costa Rica to southeastern Mexico, causing what was considered the worst natural disaster in the region since Hurricane Mitch in 1998. In the former country, rainfall totaled 2,100 millimetres (83 in) over several weeks, making the week ending October 17 the wettest in San José since 1944. Floods in Costa Rica damaged 32 bridges and roads in 174 locations, while 1,396 homes were damaged, killing seven people. In Nicaragua to the north, weeks of heavy rainfall killed 16 people and damaged or destroyed 1,333 houses. In Honduras where the tropical depression made landfall, rainfall reached 1.2 metres (3.9 ft) in some areas, although the highest official total there related to the depression was 360 millimetres (14 in) on the offshore Roatán over six days. About 40% of municipalities in the country experienced flooding, forcing over 50,000 people to leave their homes. The floods damaged about 50% of roads in Honduras, and over 10,000 houses were damaged or destroyed. Damage totaled about 3 billion lempiras (HNL, $225 million USD), and there were 60 deaths. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ...that the CIA began to recruit and train anti-Castro forces for the Bay of Pigs Invasion in the Sierra Madre mountains on the Pacific coast of Guatemala?
- ...that Castillo de los Tres Reyes Magos del Morro (pictured), a fortress which guards the entrance to Havana bay in Havana, was named after the biblical Magi?
- ...that the French West Indies refers to the two French overseas departments of Guadeloupe and Martinique, and also includes the Guadeloupean dependencies of French St. Martin, Saint-Barthélemy, Les Saintes, Marie-Galante and La Désirade?
- ... that the oldest winery in The Americas is in Parras de la Fuente?
- ... that during the Dead Rabbits Riot of 1857, residents of Mulberry Street in New York City were forced to barricade themselves in their homes?
Selected panorama

Topics
Categories
List articles
Related portals
Northern America
Central America
Caribbean
WikiProjects
 North America
North America-
 Canada
Canada -
 Greenland
Greenland -
 Mexico
Mexico -
 Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon -
 United States
United States  Central America
Central America-
 Belize
Belize -
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica -
 El Salvador
El Salvador -
 Guatemala
Guatemala -
 Honduras
Honduras -
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua -
 Panama
Panama  Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica Caribbean
Caribbean-
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda -
 Bahamas
Bahamas -
 Barbados
Barbados -
 Bermuda
Bermuda -
 Cuba
Cuba -
 Dominica
Dominica -
 Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic -
 Grenada
Grenada -
 Haiti
Haiti -
 Jamaica
Jamaica -
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico -
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis -
 Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia -
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines -
 Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus

























