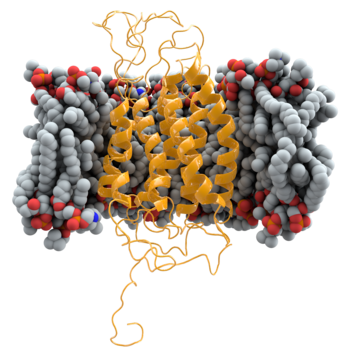
CCR5 is a human membrane protein that acts as a secondary receptor for HIV, enabling the viral and cell membranes to fuse. People with two copies of a mutated Δ32 form of CCR5 are naturally resistant to infection by most strains of HIV, and the normal form is the target of entry inhibitors such as maraviroc.
Credit: Thomas Splettstoesser (18 July 2012)