| Portal vein thrombosis | |
|---|---|
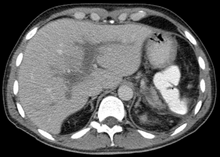 | |
| Portal vein thrombosis seen with computed tomography. | |
| Specialty | Angiology |
Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is a vascular disease of the liver that occurs when a blood clot occurs in the hepatic portal vein, which can lead to increased pressure in the portal vein system and reduced blood supply to the liver. The mortality rate is approximately 1 in 10.[1]
An equivalent clot in the vasculature that exits the liver carrying deoxygenated blood to the right atrium via the inferior vena cava, is known as hepatic vein thrombosis or Budd-Chiari syndrome.[2]
- ^ DeLeve LD, Valla DC, Garcia-Tsao G (May 2009). "Vascular disorders of the liver". Hepatology. 49 (5): 1729–1764. doi:10.1002/hep.22772. PMC 6697263. PMID 19399912.
- ^ O'Mara SR, Wiesner L. "Hepatic Disorders". In Tintinalli JE, Ma O, Yealy DM, Meckler GD, Stapczynski J, Cline DM, Thomas SH (eds.). Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (9 ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.