| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Tripotassium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.596 |
| E number | E332(ii) (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
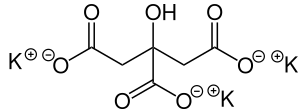
| K3C6H5O7 | |
| Molar mass | 306.395 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder hygroscopic |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.98 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K)[1] |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in glycerin insoluble in ethanol (95%) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.5 |
| Pharmacology | |
| A12BA02 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
170 mg/kg (IV, dog) 5400mg/kg (oral, rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium citrate (also known as tripotassium citrate) is a potassium salt of citric acid with the molecular formula K3C6H5O7. It is a white, hygroscopic crystalline powder. It is odorless with a saline taste. It contains 38.28% potassium by mass. In the monohydrate form, it is highly hygroscopic and deliquescent.
As a food additive, potassium citrate is used to regulate acidity, and is known as E number E332. Medicinally, it may be used to control kidney stones derived from uric acid or cystine.
In 2020, it was the 297th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.[2][3]
- ^ a b "Potassium Citrate". hazard.com. Archived from the original on 2017-08-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ "Potassium Citrate - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.