This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2020) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium selenide
| |
| Other names
Dipotassium selenide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.817 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| K2Se | |
| Molar mass | 157.16 |
| Appearance | clearish wet crystal[1] |
| Density | 2.29 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | 800 °C (1,470 °F; 1,070 K)[3] |
| reacts | |
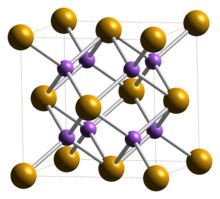
| Structure | |
| cubic: antifluorite | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
toxic |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H331, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P304+P340, P310, P314, P320, P321, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Potassium oxide Potassium sulfide Potassium telluride Potassium polonide |
Other cations
|
Lithium selenide Sodium selenide Rubidium selenide Caesium selenide |
Related compounds
|
Potassium selenate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium selenide (K2Se) is an inorganic compound formed from selenium and potassium.
- ^ Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Taschenbuch für Chemiker und Physiker. 3. Elemente, anorganische Verbindungen und Materialien, Minerale, Band 3. 4. Auflage, Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-5406-0035-0, S. 692 ([1], p. 692, at Google Books).
- ^ Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: Handbook of inorganic compounds. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-8671-8, S. 336 ([2], p. 336, at Google Books).
- ^ "Potassium selenide" (2017) at ChemicalBook (database).