| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium tetrachloridocuprate(II)
| |
| Other names
Potassium tetrachlorocuprate, potassium copper(II) tetrachloride, dipotassium cupric chloride, mitscherlichite (dihydrate mineral)
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| K2CuCl4 (anhydrous) K2CuCl4·2H2O (dihydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 319.585 g/mol (dihydrate) |
| Appearance | greenish blue crystals (dihydrate) |
| Density | 2.416 g/cm3 at 25 °C (dihydrate)[1] |
| Structure | |
| (dihydrate:) Tetragonal.Point Group: 4/m 2/m 2/m (probable). Crystals, short prismatic along [001], or pyramidal {011}, minute; in stalactitic growths[2] | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Cesium tetrachloridocuprate(II) ammonium tetrachloridocuprate(II) rubidium tetrachloridocuprate(II) iron(II) tetrachloridocuprate(II) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
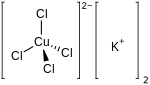
Potassium tetrachloridocuprate(II) is a salt with chemical formula K
2CuCl
4, also written as (K+
)2·[CuCl
4]2−.
The compound is often found as the dihydrate K
2CuCl
4·2H
2O, which is a brilliant greenish blue crystalline solid.[1] This form also occurs naturally as the rare mineral mitscherlichite.[1][2]
The compound is also called potassium tetrachlorocuprate(II), dipotassium tetrachlorocuprate, potassium copper(II) tetrachloride, potassium cupric chloride and other similar names.