Principality of Galilee | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1099–1187 | |||||||||
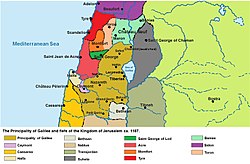 Galilee in 1187 | |||||||||
| Status | Vassal of Kingdom of Jerusalem | ||||||||
| Capital | Tiberias | ||||||||
| Common languages | Latin, Old French, Italian (also Arabic and Greek) | ||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism, Greek Orthodoxy, Syriac Orthodoxy, Islam, Judaism | ||||||||
| Government | Feudal monarchy | ||||||||
| Prince | |||||||||
• 1099–1101 | Tancred | ||||||||
• 1174–1187 | Raymond III | ||||||||
| Historical era | High Middle Ages | ||||||||
• First Crusade | 1099 | ||||||||
• Conquered by Saladin | 1187 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The principality of Galilee was one of the four major seigneuries of the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem, according to 13th-century commentator John of Ibelin, grandson of Balian.[1] The direct holdings of the principality centred around Tiberias, in Galilee proper, but with all its vassals, the lordship covered all Galilee (now Israel) and southern Phoenicia (today Lebanon). The independent Lordship of Sidon was located between Galilee's holdings. The principality also had its own vassals: the Lordships of Beirut, Nazareth, and Haifa.
The principality was established, at least in name, in 1099 when Tancred was given Tiberias, Haifa, and Bethsan by Godfrey of Bouillon. In 1101, Baldwin I limited Tancred's power by giving Haifa to Geldemar Carpenel, and Tancred was forced to give up the principality and become regent in Antioch. The principality became the fief of the families of St. Omer, Montfaucon (Falcomberques), and then Bures, and its main seat was in Tiberias; thus it was sometimes also called the Principality of Tiberias or the Tiberiad. The principality was destroyed by Saladin in 1187, although the title was used by relatives and younger sons of the kings of Cyprus (the titular kings of Jerusalem) afterwards, and some of its former holdings were briefly reclaimed by a treaty made during the Barons' Crusade.[2]
- ^ W.), Edbury, P. W. (Peter (1997). John of Ibelin and the Kingdom of Jerusalem. Woodbridge, Suffolk, UK: Boydell Press. p. 113. ISBN 0585257523. OCLC 45732821.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Edbury, P. W. (Peter W. ) (1997). John of Ibelin and the Kingdom of Jerusalem. Internet Archive. Woodbridge, Suffolk, UK ; Rochester, NY, USA : Boydell Press. pp. 59–60. ISBN 9780851157030.
