| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
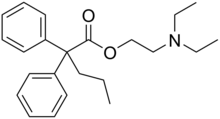
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Diethylamino)ethyl 2,2-diphenylpentanoate | |
| Other names
SKF 525-A
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H31NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 353.506 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Proadifen (SKF-525A) is a non-selective inhibitor of cytochrome P450 enzymes, preventing some types of drug metabolism.[1] It is also an inhibitor of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS), CYP-dependent (cytochrome P450-dependent) arachidonate metabolism, transmembrane calcium influx, and platelet thromboxane synthesis. Further documented effects include the blockade of ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 8 (KIR6.1), and stimulation of endothelial cell prostacyclin production.[2]
Proadifen exerts apoptotic/anti-proliferate (tumour suppressing) effects in certain forms of cancer (HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma), believed to be caused by mediation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 β (GSK-3β). In the same study administration of proadifen was demonstrated to produce time- and dose-dependent phosphatidylserine externalization, caspase-3 activation and PARP cleavage. Intense upregulation of NAG-1 and ATF3 and downregulation of Mcl-1 and Egr-1 were also observed.[3]
Proadifen has been demonstrated to normally inhibit the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (NAChR) and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (MAChR) in rats.[2]
- ^ Marshall, FN; Williamson, HE (1964). "Natruretic Response During Infusion of Beta-Diethylaminoethyl-Diphenylpropyl Acetate Hydrocloride (Skf 525-A)". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 143: 395–400. PMID 14161153.
- ^ a b "Proadifen hydrochloride (CAS 62-68-0)". Santa Cruz Biotech.
- ^ Jendželovský R, Koval J, Mikeš J, Papčová Z, Plšíková J, Fedoročko P (September 2012). "Inhibition of GSK-3β reverses the pro-apoptotic effect of proadifen (SKF-525A) in HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cells". Toxicol in Vitro. 26 (6): 775–82. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2012.05.014. PMID 22683934.