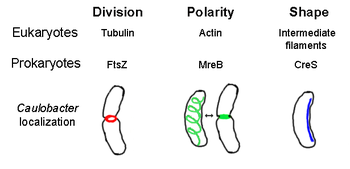
The prokaryotic cytoskeleton is the collective name for all structural filaments in prokaryotes. It was once thought that prokaryotic cells did not possess cytoskeletons, but advances in visualization technology and structure determination led to the discovery of filaments in these cells in the early 1990s.[2] Not only have analogues for all major cytoskeletal proteins in eukaryotes been found in prokaryotes, cytoskeletal proteins with no known eukaryotic homologues have also been discovered.[3][4][5][6] Cytoskeletal elements play essential roles in cell division, protection, shape determination, and polarity determination in various prokaryotes.[7][8]
- ^ Gitai Z (March 2005). "The new bacterial cell biology: moving parts and subcellular architecture". Cell. 120 (5): 577–86. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.026. PMID 15766522. S2CID 8894304.
- ^ Bi EF, Lutkenhaus J (November 1991). "FtsZ ring structure associated with division in Escherichia coli". Nature. 354 (6349): 161–4. Bibcode:1991Natur.354..161B. doi:10.1038/354161a0. PMID 1944597. S2CID 4329947.
- ^ Gunning PW, Ghoshdastider U, Whitaker S, Popp D, Robinson RC (June 2015). "The evolution of compositionally and functionally distinct actin filaments". Journal of Cell Science. 128 (11): 2009–19. doi:10.1242/jcs.165563. PMID 25788699.
- ^ Popp D, Narita A, Lee LJ, Ghoshdastider U, Xue B, Srinivasan R, Balasubramanian MK, Tanaka T, Robinson RC (June 2012). "Novel actin-like filament structure from Clostridium tetani". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (25): 21121–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.341016. PMC 3375535. PMID 22514279.
- ^ Popp D, Narita A, Ghoshdastider U, Maeda K, Maéda Y, Oda T, Fujisawa T, Onishi H, Ito K, Robinson RC (April 2010). "Polymeric structures and dynamic properties of the bacterial actin AlfA". Journal of Molecular Biology. 397 (4): 1031–41. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.02.010. PMID 20156449.
- ^ Wickstead B, Gull K (August 2011). "The evolution of the cytoskeleton". The Journal of Cell Biology. 194 (4): 513–25. doi:10.1083/jcb.201102065. PMC 3160578. PMID 21859859.
- ^ Shih YL, Rothfield L (September 2006). "The bacterial cytoskeleton". Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 70 (3): 729–54. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00017-06. PMC 1594594. PMID 16959967.
- ^ Michie KA, Löwe J (2006). "Dynamic filaments of the bacterial cytoskeleton" (PDF). Annual Review of Biochemistry. 75: 467–92. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142452. PMID 16756499. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 17, 2006.