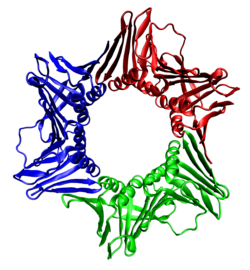
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a DNA clamp that acts as a processivity factor for DNA polymerase δ in eukaryotic cells and is essential for replication. PCNA is a homotrimer and achieves its processivity by encircling the DNA, where it acts as a scaffold to recruit proteins involved in DNA replication, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling and epigenetics.[5]
Many proteins interact with PCNA via the two known PCNA-interacting motifs PCNA-interacting peptide (PIP) box[6] and AlkB homologue 2 PCNA interacting motif (APIM).[7] Proteins binding to PCNA via the PIP-box are mainly involved in DNA replication whereas proteins binding to PCNA via APIM are mainly important in the context of genotoxic stress.[8]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000132646 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027342 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Moldovan GL, Pfander B, Jentsch S (May 2007). "PCNA, the maestro of the replication fork". Cell. 129 (4): 665–679. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.003. PMID 17512402. S2CID 3547069.
- ^ Warbrick E (March 1998). "PCNA binding through a conserved motif". BioEssays. 20 (3): 195–199. doi:10.1002/(sici)1521-1878(199803)20:3<195::aid-bies2>3.0.co;2-r. PMID 9631646.
- ^ Gilljam KM, Feyzi E, Aas PA, Sousa MM, Müller R, Vågbø CB, et al. (September 2009). "Identification of a novel, widespread, and functionally important PCNA-binding motif". The Journal of Cell Biology. 186 (5): 645–654. doi:10.1083/jcb.200903138. PMC 2742182. PMID 19736315.
- ^ Mailand N, Gibbs-Seymour I, Bekker-Jensen S (May 2013). "Regulation of PCNA-protein interactions for genome stability". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 14 (5): 269–282. doi:10.1038/nrm3562. PMID 23594953. S2CID 25952152.