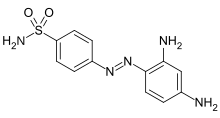
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Sulfamidochrysoïdine, Rubiazol, Prontosil rubrum, Aseptil rojo, Streptocide, Sulfamidochrysoïdine hydrochloride |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.802 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H13N5O2S |
| Molar mass | 291.33 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Prontosil is an antibacterial drug of the sulfonamide group. It has a relatively broad effect against gram-positive cocci but not against enterobacteria. One of the earliest antimicrobial drugs, it was widely used in the mid-20th century but is little used today because better options now exist. The discovery and development of this first sulfonamide drug opened a new era in medicine,[1] because it greatly widened the success of antimicrobial chemotherapy in an era when many physicians doubted its still largely untapped potential. At the time, disinfectant cleaners and topical antiseptic wound care were widely used but there were very few antimicrobial drugs to use safely inside living bodies. Antibiotic drugs derived from microbes, which are relied on heavily today, did not yet exist. Prontosil was discovered in 1932[2] by a research team at the Bayer Laboratories of the IG Farben conglomerate in Germany led by Gerhard Domagk. Domagk received the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for that discovery.[3]
- ^ Hager T (2006). The Demon Under the Microscope: From Battlefield Hospitals to Nazi Labs, One Doctor's Heroic Search for the World's First Miracle Drug. Harmony Books. ISBN 1-4000-8214-5.
- ^ Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology. OUP Oxford. 2009. p. 56. ISBN 9780191039621.
- ^ "Physiology or Medicine 1939 – Presentation Speech". Nobel Foundation. Archived from the original on 14 January 2015. Retrieved 14 January 2015.