 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Amoglandin, Croniben, Cyclosin, Dinifertin, Enzaprost, Glandin, PGF2α, Panacelan, Prostamodin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous (cannot used to induce labor)because it cannot be used in cervix, intra-amniotic (to induce abortion) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 3 to 6 hours in amniotic fluid, less than 1 minute in blood plasma |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.209.720 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
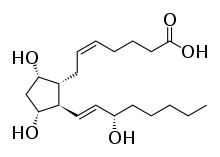
| Formula | C20H34O5 |
| Molar mass | 354.487 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Solubility in water | 200 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α in prostanoid nomenclature), pharmaceutically termed dinoprost, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin used in medicine to induce labor and as an abortifacient.[1] Prostaglandins are lipids throughout the entire body that have a hormone-like function.[2] In pregnancy, PGF2α is medically used to sustain contracture and provoke myometrial ischemia to accelerate labor and prevent significant blood loss in labor.[3] Additionally, PGF2α has been linked to being naturally involved in the process of labor. It has been seen that there are higher levels of PGF2α in maternal fluid during labor when compared to at term.[4] This signifies that there is likely a biological use and significance to the production and secretion of PGF2α in labor. Prostaglandin is also used to treat uterine infections in domestic animals.
In domestic mammals, it is produced by the uterus when stimulated by oxytocin, in the event that there has been no implantation during the luteal phase. It acts on the corpus luteum to cause luteolysis, forming a corpus albicans and stopping the production of progesterone. Action of PGF2α is dependent on the number of receptors on the corpus luteum membrane.
The PGF2α isoform 8-iso-PGF2α was found in significantly increased amounts in patients with endometriosis, thus being a potential causative link in endometriosis-associated oxidative stress.[5]
- ^ O'Neil MJ, ed. (2013). The Merck index: an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals (15th ed.). Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 978-1849736701. OCLC 824530529.
- ^ "Prostaglandin". Britannica. September 28, 2022. Retrieved November 6, 2022.
- ^ Kerekes L, Domokos N (July 1979). "The effect of prostaglandin F2 alpha on third stage labor". Prostaglandins. 18 (1): 161–166. doi:10.1016/S0090-6980(79)80034-9. PMID 392622.
- ^ Sahmay S, Coke A, Hekim N, Atasu T (1988). "Maternal, umbilical, uterine and amniotic prostaglandin E and F2 alpha levels in labour". The Journal of International Medical Research. 16 (4): 280–285. doi:10.1177/030006058801600405. PMID 3169373. S2CID 73028858.
- ^ Sharma I, Dhaliwal LK, Saha SC, Sangwan S, Dhawan V (June 2010). "Role of 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha and 25-hydroxycholesterol in the pathophysiology of endometriosis". Fertility and Sterility. 94 (1): 63–70. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.01.141. PMID 19324352.