| |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Federated state |
| Number |
|
| Government | |
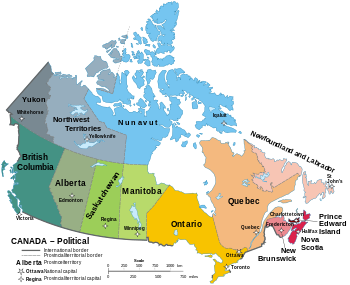
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.
The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the Constitution Act, 1867 (formerly[1] called the British North America Act, 1867), whereas territories are federal territories whose governments are creatures of statute with powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada. The powers flowing from the Constitution Act are divided between the Government of Canada (the federal government) and the provincial governments to exercise exclusively. A change to the division of powers between the federal government and the provinces requires a constitutional amendment, whereas a similar change affecting the territories can be performed unilaterally by the Parliament of Canada or government.
In modern Canadian constitutional theory, the provinces are considered to be co-sovereign within certain areas based on the divisions of responsibility between the provincial and federal government within the Constitution Act, 1867, and each province thus has its own representative of the Canadian Crown, the lieutenant governor. The territories are not sovereign, but instead their authorities and responsibilities are devolved directly from the federal level, and as a result, have a commissioner that represents the federal government.
- ^ Name changed only in Canada by the Canada Act 1982 (UK), s. 1