| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Pegasus |
| Right ascension | 23h 57m 45.52681s[1] |
| Declination | 25° 08′ 29.0480″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.66[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M3III[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.66[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.59[2] |
| Variable type | suspected[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −6.59±0.23[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −35.24[1] mas/yr Dec.: −31.60[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 6.85 ± 0.24 mas[1] |
| Distance | 480 ± 20 ly (146 ± 5 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | –1.19[6] |
| Orbit[7] | |
| Period (P) | 55.06±11.31 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 0.170±0.016″ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.19±0.10 |
| Inclination (i) | 65.6±2.2° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 46.6±2.3° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,001.83±8.81 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 159.7±11.9° |
| Details | |
| Radius | 98±6[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 960[6] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,882[9] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
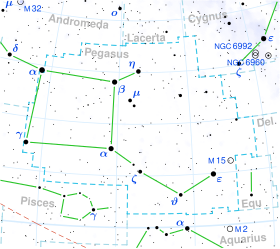
Psi Pegasi, which is Latinized from ψ Pegasi, is a binary star system within the great square[11] in the northern constellation of Pegasus. It has a red hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.66.[2] This object is located at a distance of approximately 476 light-years away from the Sun based on parallax,[1] but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −6.6 km/s.[5]

The orbital elements for this system were computed for the first time in 2004 based on interferometric observations, yielding an orbital period of roughly 55 years and an eccentricity of about 0.19.[7][13][14] The visible component is an aging red giant star on the asymptotic giant branch[15] with a stellar classification of M3III.[3] It is a suspected variable, probably semiregular, with its magnitude varying from 4.63 to 4.69[4][16] over periods of 37.4 and 118.9 days.[12] With the supply of hydrogen exhausted at its core, the star has cooled and expanded to around 98[8] times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 960[6] times the luminosity of the Sun from its bloated photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,882 K.[9]
- ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
vanLeeuwen2007was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
Ducati2002was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
perkins1989was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
gcvswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Famaey2005was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
XHIPwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Olevic2004was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
ArroyoTorres2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Perez2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Harrington2010was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Tabur2009was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Malkov2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
WDSwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Eggen1992was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
aavsowas invoked but never defined (see the help page).