| |||
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pyridine[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Azabenzene | |||
| Other names
Azine
Azinine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.464 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H5N | |||
| Molar mass | 79.102 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[2] | ||
| Odor | Nauseating, fish-like[3] | ||
| Density | 0.9819 g/mL (20 °C)[4] | ||
| Melting point | −41.63 °C (−42.93 °F; 231.52 K)[4] | ||
| Boiling point | 115.2 °C (239.4 °F; 388.3 K)[4] | ||
| Miscible[4] | |||
| log P | 0.65[5] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 16 mmHg (20 °C)[3] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 5.23 (pyridinium)[6] | ||
| Conjugate acid | Pyridinium | ||
| −48.7·10−6 cm3/mol[7] | |||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.166 W/(m·K)[8] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5095 (20 °C)[4] | ||
| Viscosity | 0.879 cP (25 °C)[9] | ||
| 2.215 D[10] | |||
| Thermochemistry[11] | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
132.7 J/(mol·K) | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
100.2 kJ/mol | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.782 MJ/mol | ||
| Hazards[15] | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Low to moderate hazard[13] | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  [12] [12]
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H302, H312, H315, H319, H332[12] | |||
| P210, P280, P301+P312, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340+P312, P305+P351+P338[12] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 20 °C (68 °F; 293 K)[16] | ||
| 482 °C (900 °F; 755 K)[16] | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.8–12.4%[3] | ||
Threshold limit value (TLV)
|
5 ppm (TWA) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
891 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1500 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 1580 mg/kg (rat, oral)[14] | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
9000 ppm (rat, 1 hr)[14] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 5 ppm (15 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 5 ppm (15 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1000 ppm[3] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related amines
|
Picoline Quinoline | ||
Related compounds
|
Aniline Pyrimidine Piperidine | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Pyridine (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
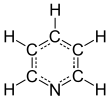
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom (=N−). It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity.[page needed][17] The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.[2]
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 141. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
ulwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0541". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c d e Haynes, p. 3.474
- ^ Haynes, p. 5.176
- ^ Haynes, p. 5.95
- ^ Haynes, p. 3.579
- ^ Haynes, p. 6.258
- ^ Haynes, p. 6.246
- ^ Haynes, p. 9.65
- ^ Haynes, pp. 5.34, 5.67
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
GESTISwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Pyridine: main hazards, precautions and toxicity
- ^ a b "Pyridine". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Pyridine MSDS". fishersci.com. Fisher. Archived from the original on 11 June 2010. Retrieved 2 February 2010.
- ^ a b Haynes, p. 15.19
- ^ Vaganova, Evgenia; Eliaz, Dror; Shimanovich, Ulyana; Leitus, Gregory; Aqad, Emad; Lokshin, Vladimir; Khodorkovsky, Vladimir (January 2021). "Light-Induced Reactions within Poly(4-vinyl pyridine)/Pyridine Gels: The 1,6-Polyazaacetylene Oligomers Formation". Molecules. 26 (22): 6925. doi:10.3390/molecules26226925. ISSN 1420-3049. PMC 8621047. PMID 34834017.