| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pyrimidine[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,3-Diazabenzene | |||
| Other names
1,3-Diazine
m-Diazine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.479 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | pyrimidine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 80.088 g mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.016 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | 20 to 22 °C (68 to 72 °F; 293 to 295 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 123 to 124 °C (253 to 255 °F; 396 to 397 K) | ||
| Miscible (25°C) | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.10[2] (protonated pyrimidine) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
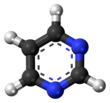
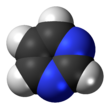
Pyrimidine (C4H4N2; /pɪˈrɪ.mɪˌdiːn, paɪˈrɪ.mɪˌdiːn/) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (C5H5N).[3] One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring.[4]: 250 The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions).
In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U).
- ^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 141. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Brown, H. C.; et al. (1955). Baude, E. A.; F. C., Nachod (eds.). Determination of Organic Structures by Physical Methods. New York, NY: Academic Press.
- ^ Gilchrist, Thomas Lonsdale (1997). Heterocyclic chemistry. New York: Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-27843-1.
- ^ Joule, John A.; Mills, Keith, eds. (2010). Heterocyclic Chemistry (5th ed.). Oxford: Wiley. ISBN 978-1-405-13300-5.