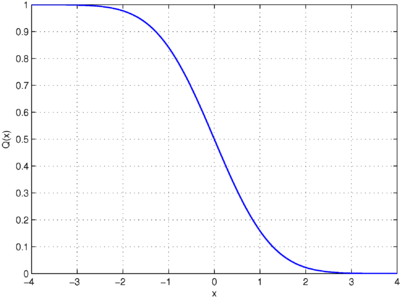
In statistics, the Q-function is the tail distribution function of the standard normal distribution.[1][2] In other words, is the probability that a normal (Gaussian) random variable will obtain a value larger than standard deviations. Equivalently, is the probability that a standard normal random variable takes a value larger than .
If is a Gaussian random variable with mean and variance , then is standard normal and
where .
Other definitions of the Q-function, all of which are simple transformations of the normal cumulative distribution function, are also used occasionally.[3]
Because of its relation to the cumulative distribution function of the normal distribution, the Q-function can also be expressed in terms of the error function, which is an important function in applied mathematics and physics.
- ^ "The Q-function". cnx.org. Archived from the original on 2012-02-29.
- ^ "Basic properties of the Q-function" (PDF). 2009-03-05. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-25.
- ^ Normal Distribution Function – from Wolfram MathWorld







