| QF 6-inch 40 calibre naval gun 15 cm/40 (6") 41st Year Type | |
|---|---|
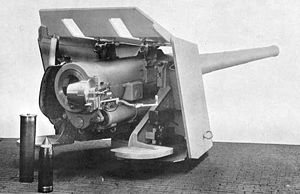 Typical naval deck mounting. An early long cartridge case for gunpowder propellant is upended at bottom left, a shell stands next to the cartridge. | |
| Type | Naval gun Coast defence gun |
| Place of origin | United Kingdom licence-produced in Japan |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1892–1945 |
| Used by | Royal Navy Imperial Japanese Navy Chilean Navy Italian Navy Argentine Navy United States Romanian Navy Royal Canadian Navy |
| Wars | Russo-Japanese War World War I World War II |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Elswick Ordnance Company Royal Arsenal, Woolwich |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 6.6 tons |
| Barrel length | 240 inches (6.096 m) bore |
| Shell | QF, separate cartridge and shell |
| Shell weight | 100 pounds (45 kg) |
| Calibre | 6-inch (152mm) |
| Elevation | -5 / +20 degrees |
| Traverse | +150 / -150 degrees |
| Rate of fire | 5–7 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 2,154 feet per second (657 m/s)[1] 820 feet per second (250 m/s) for anti-submarine shells |
| Effective firing range | 10,000 yards (9,140 m) at 20°elevation; 15,000 yards (13,700 m) at 28°elevation |
The QF 6-inch 40 calibre naval gun (Quick-Firing) was used by many United Kingdom-built warships around the end of the 19th century and the start of the 20th century. In British service it was known as the QF 6-inch Mk I, II, III guns.[note 1] As the 15 cm/40 (6") 41st Year Type naval gun it was used for pre-dreadnought battleships, armoured cruisers and protected cruisers of the early Imperial Japanese Navy built in UK and European shipyards. It was also the heaviest gun ever carried by a pre-Cold War destroyer.
- ^ 2154 ft/second in British service firing 100 lb (45 kg) projectile, using 13 lb 4 oz (6.0 kg) Cordite size 30 propellant, at 60 °F (16 °C). 1,882 ft/s (574 m/s) using 27 lb 12 oz (12.6 kg) gunpowder propellant. From Text Book of Gunnery, 1902.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).