This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Qin
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9th century BC–207 BC | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Capital | |||||||||||
| Common languages | Old Chinese | ||||||||||
| Religion | |||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 9th century BC | ||||||||||
• Founded by Feizi | 860 BCE? | ||||||||||
• Declared empire | 221 BC | ||||||||||
• defunct | 207 BC | ||||||||||
| Currency | ancient Chinese coinage | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | China | ||||||||||
| Qin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Qin" in seal script (top) and regular script (bottom) characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 秦 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
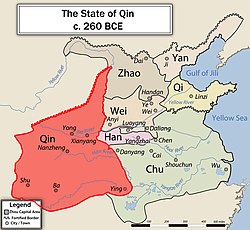
Qin (/tʃɪn/, or Ch'in[1]) was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. It is traditionally dated to 897 BC.[2] The Qin state originated from a reconquest of western lands that had previously been lost to the Xirong. Its location at the western edge of Chinese civilisation allowed for expansion and development that was not available to its rivals in the North China Plain.
After extensive reform during the 4th century BC, Qin emerged as one of the dominant powers among the Seven Warring States. It unified the seven states of China in 221 BC under Qin Shi Huang. This unification established the Qin dynasty, which, despite its short duration, had a significant influence on later Chinese history. Accordingly, the Qin state before the Qin dynasty was established is also referred to as the "predynastic Qin"[3][4] or "proto-Qin".[5]
- ^ Joseph Richmond Levenson (1969). China: An Interpretive History. University of California Press. p. 66.
- ^ The Cambridge History of China: Volume 1, The Ch'in and Han Empires Google Books
- ^ Gideon Shelach-Lavi (2015). The Archaeology of Early China. Cambridge University Press. p. 314. ISBN 9780521196895.
- ^ Zhixin Sun (2017). Age of Empires: Art of the Qin and Han Dynasties. Metropolitan Museum of Art. p. 33. ISBN 9781588396174.
- ^ Lothar von Falkenhausen (2006). Chinese Society in the Age of Confucius (1000-250 BC). Cotsen Institute of Archaeology Press. p. 235. ISBN 9781938770456.