| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Quinazoline[1] | |||
| Other names
1,3-diazanaphthalene
benzopyrimidine phenmiazine benzo-1,3-diazine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.424 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H6N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 130.150 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | light yellow crystals | ||
| Density | 1.351 g/cm3, solid | ||
| Melting point | 48 °C (118 °F; 321 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 243 °C (469 °F; 516 K) | ||
| Soluble | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.51[2] | ||
| Structure | |||
| 2.2 D[3] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Irritant | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| Flash point | 106 °C (223 °F; 379 K) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
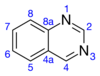
Quinazoline is an organic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is an aromatic heterocycle with a bicyclic structure consisting of two fused six-membered aromatic rings, a benzene ring and a pyrimidine ring. It is a light yellow crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Also known as 1,3-diazanaphthalene, quinazoline received its name from being an aza derivative of quinoline. Though the parent quinazoline molecule is rarely mentioned by itself in technical literature, substituted derivatives have been synthesized for medicinal purposes such as antimalarial and anticancer agents. Quinazoline is a planar molecule. It is isomeric with the other diazanaphthalenes of the benzodiazine subgroup: cinnoline, quinoxaline, and phthalazine. Over 200 biologically active quinazoline and quinoline alkaloids are identified.[4][5]
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 212. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Armarego, W. L. F. (1963). "Quinazolines". Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry Volume 1. Vol. 1. pp. 253–309. doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60527-9. ISBN 9780120206018. PMID 14087221.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Houben-Weylwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Shang, XF; Morris-Natschke, SL; Liu, YQ; Guo, X; Xu, XS; Goto, M; Li, JC; Yang, GZ; Lee, KH (May 2018). "Biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids part I." Medicinal Research Reviews. 38 (3): 775–828. doi:10.1002/med.21466. PMC 6421866. PMID 28902434.
- ^ Shang, Xiao-Fei; Morris-Natschke, Susan L.; Yang, Guan-Zhou; Liu, Ying-Qian; Guo, Xiao; Xu, Xiao-Shan; Goto, Masuo; Li, Jun-Cai; Zhang, Ji-Yu; Lee, Kuo-Hsiung (September 2018). "Biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids part II". Medicinal Research Reviews. 38 (5): 1614–1660. doi:10.1002/med.21492. ISSN 0198-6325. PMC 6105521. PMID 29485730.

