 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Quinaglute, Quinidex |
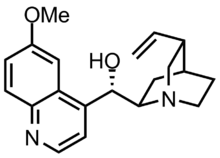
| Other names | (2-Ethenyl-4-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-5-yl)-(6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)-methanol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intramuscular injection, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 70–85% |
| Metabolism | 50–90% (by liver) |
| Elimination half-life | 6–8 hours |
| Excretion | By the liver (20% as unchanged quinidine via urine) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.254 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H24N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 324.424 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Quinidine is a class IA antiarrhythmic agent used to treat heart rhythm disturbances.[1] It is a diastereomer of antimalarial agent quinine,[2] originally derived from the bark of the cinchona tree. The drug causes increased action potential duration, as well as a prolonged QT interval. As of 2019, its IV formulation is no longer being manufactured for use in the United States.[3]
- ^ Grace AA, Camm AJ (January 1998). "Quinidine". The New England Journal of Medicine. 338 (1): 35–45. doi:10.1056/NEJM199801013380107. PMID 9414330.
- ^ Shiomi S, Misaka R, Kaneko M, Ishikawa H (November 2019). "Enantioselective total synthesis of the unnatural enantiomer of quinine". Chemical Science. 10 (41): 9433–9437. doi:10.1039/c9sc03879e. PMC 7020653. PMID 32110303.
- ^ "Artesunate Now First-Line Treatment for Severe Malaria in the United States". CDC Online Newsroom. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 28 March 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2019.