| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Quinoxaline[1] | |||
| Other names
Benzo[b]pyrazine, Benzopyrazine, Benzoparadiazine, 1,4-Benzodiazine, Phenopiazine, Phenpiazine, Quinazine, Chinoxalin
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.862 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H6N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 130.150 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 29-32 °C | ||
| Boiling point | 220 to 223 °C (428 to 433 °F; 493 to 496 K) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.60[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
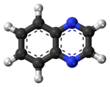
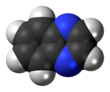
A quinoxaline, also called a benzopyrazine, in organic chemistry, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine ring. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinazoline, phthalazine and cinnoline.[3] It is a colorless oil that melts just above room temperature. Although quinoxaline itself is mainly of academic interest, quinoxaline derivatives are used as dyes, pharmaceuticals (such as varenicline), and antibiotics such as olaquindox, carbadox, echinomycin, levomycin and actinoleutin.
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 212. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Brown, H.C.; et al. (1955). Baude, E.A.; Nachod, F.C. (eds.). Determination of Organic Structures by Physical Methods. New York: Academic Press.
- ^ One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Quinoxalines". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 22 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 760.