| RNA silencing suppressor p19 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
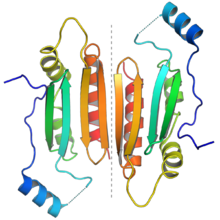 The protein dimer formed by two p19 molecules. Each monomer is colored from N-terminus (blue) to C-terminus (red) to illustrate the end-to-end orientation of the dimer. The dotted gray line in the center highlights the dimer interface. From PDB: 1R9F.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Tombus_p19 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF03220 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR004905 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
RNA silencing suppressor p19 (also known as Tombusvirus P19 core protein and 19 kDa symptom severity modulator) is a protein expressed from the ORF4 gene in the genome of tombusviruses. These viruses are positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses that infect plant cells, in which RNA silencing forms a widespread and robust antiviral defense system. The p19 protein serves as a counter-defense strategy, specifically binding the 19- to 21-nucleotide double-stranded RNAs that function as small interfering RNA (siRNA) in the RNA silencing system. By sequestering siRNA, p19 suppresses RNA silencing and promotes viral proliferation.[1][2][3] The p19 protein is considered a significant virulence factor[4] and a component of an evolutionary arms race between plants and their pathogens.[5]
- ^ a b Ye K, Malinina L, Patel DJ (December 2003). "Recognition of small interfering RNA by a viral suppressor of RNA silencing". Nature. 426 (6968): 874–8. Bibcode:2003Natur.426..874Y. doi:10.1038/nature02213. PMC 4694583. PMID 14661029.
- ^ Vargason JM, Szittya G, Burgyán J, Hall TM (December 2003). "Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor". Cell. 115 (7): 799–811. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00984-X. PMID 14697199. S2CID 12993441.
- ^ Lakatos L, Szittya G, Silhavy D, Burgyán J (February 2004). "Molecular mechanism of RNA silencing suppression mediated by p19 protein of tombusviruses". The EMBO Journal. 23 (4): 876–84. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600096. PMC 381004. PMID 14976549.
- ^ Scholthof HB (May 2006). "The Tombusvirus-encoded P19: from irrelevance to elegance". Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 4 (5): 405–11. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1395. PMID 16518419. S2CID 30361458.
- ^ Pumplin N, Voinnet O (November 2013). "RNA silencing suppression by plant pathogens: defence, counter-defence and counter-counter-defence". Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 11 (11): 745–60. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3120. PMID 24129510. S2CID 205498691.