| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Corvus |
| Right ascension | 12h 37m 40.711s[2] |
| Declination | −19° 34′ 40.03″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.77[3] (8.6 - 9.16)[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Main sequence |
| Spectral type | F0V[5] (F0 + G0)[6] |
| B−V color index | 0.404±0.026[3] |
| Variable type | β Lyr[7] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 19.0±4.6[8] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −29.326 mas/yr[2] Dec.: 8.954 mas/yr[2] |
| Parallax (π) | 4.7351 ± 0.0812 mas[2] |
| Distance | 690 ± 10 ly (211 ± 4 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 2.32[3] |
| Orbit[9] | |
| Period (P) | 0.7473 d |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.00 |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2445792.3578 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 0.00° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 64 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 235 km/s |
| Details | |
| Primary | |
| Mass | 1.64±0.14[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.16 or 2.18 ± 0.08[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 8.4 or 8.5 ± 0.6[9] L☉ |
| Secondary | |
| Mass | 0.44±0.03[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.19 or 1.20 ±0.04[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.2 or 1.5 ± 0.1[9] L☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
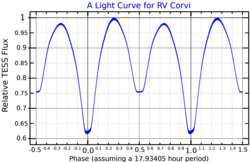
RV Corvi is an eclipsing binary star system in the southern constellation of Corvus. The brightness of the pair regularly ranges in apparent visual magnitude from 8.6 down to 9.16 over a period 18 hours,[4] even the brightest of which is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. The system is located at a distance of approximately 690 light-years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of ~19 km/s.[8]
The variability of this system was discovered by H. H. Swope.[11] In 1942, Irene G. Buttery published an orbital period of 0.74728 days for the system, showing this is an eclipsing binary.[12] It is a near-contact binary with both stars showing the effect of tidal interactions and the facing sides are less than 10% of the orbital separation apart, but are not in contact.[13] One or both stars may show an excess of luminosity on their facing sides.[9] The system is composed of stars of spectral types F0 and G0, which orbit each other every 0.7473 days.[6]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
MASTwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
GaiaDR2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Anderson_Francis_2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
AAVSORVwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Houk_Smith-Moore_1978was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
aaa446_2_785was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Samus_et_al_2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Gontcharov2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h Cite error: The named reference
McFarlane_et_al_1986was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Abhyankar_et_al_1974was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Buttery1942was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Shaw_et_al_1996was invoked but never defined (see the help page).