This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (May 2022) |
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Prandin, Novonorm, Enyglid, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a600010 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 56% (oral) |
| Protein binding | >98% |
| Metabolism | Liver oxidation and glucuronidation (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 1 hour |
| Excretion | Fecal (90%) and kidney (8%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.190 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
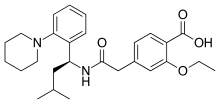
| Formula | C27H36N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 452.595 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 126 to 128 °C (259 to 262 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Repaglinide is an antidiabetic drug in the class of medications known as meglitinides, and was invented in 1983. Repaglinide is a medication used in addition to diet and exercise for blood sugar control in type 2 diabetes.[1] The mechanism of action of repaglinide involves promoting insulin release from β-islet cells of the pancreas; like other antidiabetic drugs, a main side effect concern is hypoglycemia.[1] It is sold by Novo Nordisk under the name of Prandin in the United States, Gluconorm in Canada, Surepost in Japan, Repaglinide in Egypt, and Novonorm elsewhere. In Japan it is produced by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma.[2][failed verification]
- ^ a b "DailyMed - Repaglinide - repaglinide tablet". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- ^ "Welcome to Novo Nordisk A/S". Novo Nordisk A/S. Retrieved 2015-11-05.