This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (November 2017) |  |
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (March 2018) |
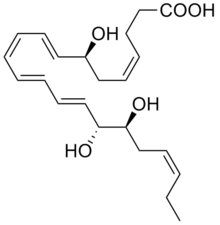
Resolvins are specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) derived from omega-3 fatty acids, primarily eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), as well as from two isomers of docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), one omega-3 and one omega-6 fatty acid. As autacoids similar to hormones acting on local tissues, resolvins are under preliminary research for their involvement in promoting restoration of normal cellular function following the inflammation that occurs after tissue injury.[1][2] Resolvins belong to a class of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) metabolites termed specialized proresolving mediators (SPMs).[3][4]
- ^ Moro, K; Nagahashi, M; Ramanathan, R; Takabe, K; Wakai, T (2016). "Resolvins and omega three polyunsaturated fatty acids: Clinical implications in inflammatory diseases and cancer". World Journal of Clinical Cases. 4 (7): 155–164. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v4.i7.155. PMC 4945585. PMID 27458590.
- ^ Balta, M. G; Loos, B. G; Nicu, E. A (2017). "Emerging Concepts in the Resolution of Periodontal Inflammation: A Role for Resolvin E1". Frontiers in Immunology. 8: 1682. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01682. PMC 5735081. PMID 29312286.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ReferenceAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Duvall, M. G.; Levy, B. D. (2015). "DHA- and EPA-derived resolvins, protectins, and maresins in airway inflammation". European Journal of Pharmacology. 785: 144–155. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.11.001. PMC 4854800. PMID 26546247.