| Retroviral ribonuclease H | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
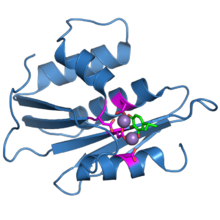 The ribonuclease H domain from the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase protein. The four active-site carboxylate residues are shown in magenta. Two bound manganese ions are shown as purple spheres. A bound inhibitor molecule, beta-thujaplicinol, is shown in green.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.1.26.13 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9050-76-4 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The retroviral ribonuclease H (retroviral RNase H) is a catalytic domain of the retroviral reverse transcriptase (RT) enzyme. The RT enzyme is used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from the retroviral RNA genome. This process is called reverse transcription. To complete this complex process, the retroviral RT enzymes need to adopt a multifunctional nature. They therefore possess 3 of the following biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, ribonuclease H, and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities.[2] Like all RNase H enzymes, the retroviral RNase H domain cleaves DNA/RNA duplexes and will not degrade DNA or unhybridized RNA.