 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Undetermined |
| Protein binding | Nearly 100% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, CYP3A4 involved |
| Elimination half-life | Variable: 6 to 9 days with normal BMI 16 days if BMI >30 |
| Excretion | Fecal (86%) and renal (3%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.210.978 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
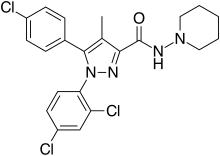
| Formula | C22H21Cl3N4O |
| Molar mass | 463.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Rimonabant (also known as SR141716; trade names Acomplia, Zimulti)[3] is an anorectic antiobesity drug approved in Europe in 2006 but was withdrawn worldwide in 2008 due to serious psychiatric side effects; it was never approved in the United States.[1][2] Rimonabant is an inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 and was first-in-class for clinical development.[4][5]
- ^ a b Sam AH, Salem V, Ghatei MA (2011). "Rimonabant: From RIO to Ban". Journal of Obesity. 2011: 432607. doi:10.1155/2011/432607. PMC 3136184. PMID 21773005.
- ^ a b Moreira FA, Crippa JA (June 2009). "The psychiatric side-effects of rimonabant". Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria. 31 (2): 145–153. doi:10.1590/s1516-44462009000200012. PMID 19578688.
- ^ "Rimonabant". AdisInsight. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ^ Fong TM, Heymsfield SB (September 2009). "Cannabinoid-1 receptor inverse agonists: current understanding of mechanism of action and unanswered questions". International Journal of Obesity. 33 (9): 947–955. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.132. PMID 19597516.
- ^ "European Approval Comes Early for Sanofi-Aventis' Acomplia". IHS. June 23, 2006.