| Rotational frequency | |
|---|---|
 | |
Other names | rotational speed, rate of rotation |
Common symbols | , n |
| SI unit | Hz |
Other units | rpm, cps |
| In SI base units | s-1 |
Derivations from other quantities | ν=ω/(2π rad), n=dN/dt |
| Dimension | |
| Part of a series on |
| Classical mechanics |
|---|
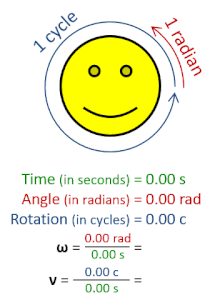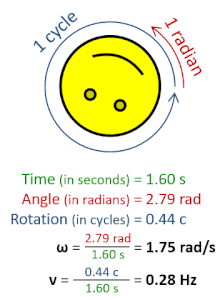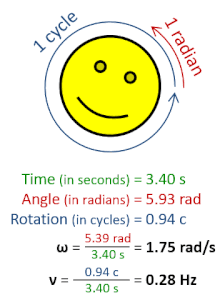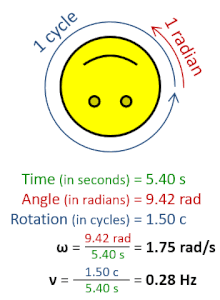
Rotational frequency, also known as rotational speed or rate of rotation (symbols ν, lowercase Greek nu, and also n), is the frequency of rotation of an object around an axis. Its SI unit is the reciprocal seconds (s−1); other common units of measurement include the hertz (Hz), cycles per second (cps), and revolutions per minute (rpm).[1][a][b]
Rotational frequency can be obtained dividing angular frequency, ω, by a full turn (2π radians): ν=ω/(2π rad). It can also be formulated as the instantaneous rate of change of the number of rotations, N, with respect to time, t: n=dN/dt (as per International System of Quantities).[4] Similar to ordinary period, the reciprocal of rotational frequency is the rotation period or period of rotation, T=ν−1=n−1, with dimension of time (SI unit seconds).
Rotational velocity is the vector quantity whose magnitude equals the scalar rotational speed. In the special cases of spin (around an axis internal to the body) and revolution (external axis), the rotation speed may be called spin speed and revolution speed, respectively.
Rotational acceleration is the rate of change of rotational velocity; it has dimension of squared reciprocal time and SI units of squared reciprocal seconds (s−2); thus, it is a normalized version of angular acceleration and it is analogous to chirpyness.
- ^ Atkins, Tony; Escudier, Marcel (2013). A Dictionary of Mechanical Engineering. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199587438.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
NISTGuide_2009was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIBrochure_9was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "ISO 80000-3:2019 Quantities and units — Part 3: Space and time" (2 ed.). International Organization for Standardization. 2019. Retrieved 2019-10-23. [1] (11 pages)
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).


