| Rozellida | |
|---|---|
| |
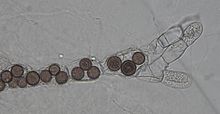
| Rozella allomycis parasitizing the chytrid Allomyces sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | Rozellomycota James & Berbee 2011 ex Doweld 2013[1]
|
| Class: | Rozellidea Cavalier-Smith 2013
|
| Order: | Rozellida Cavalier-Smith 2013 non Lara et al. 2010
|
| Family: | Rozellidae Cavalier-Smith 2013
|
| Genus | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Cryptomycota ('hidden fungi'), Rozellida, or Rozellomycota are a clade of micro-organisms that are either fungi or a sister group to fungi. They differ from classical fungi in that they lack chitinous cell walls at any trophic stage in their lifecycle, as reported by Jones and colleagues in 2011.[2][3] Despite their unconventional feeding habits,[clarification needed] chitin has been observed in the inner layer of resting spores, and in immature resting spores for some species of Rozella, as indicated with calcofluor-white stain as well as the presence of a fungal-specific chitin synthase gene.[4]
Rozellida were first detected as DNA sequences retrieved from a freshwater laboratory enclosure. Phylogenetic analysis of these sequences formed a unique terminal clade of then unknown affiliation provisionally called after the first clone in the clade: LKM11.[5]
The only formally described genus in the clade is Rozella, which was previously considered a chytrid. The existence of related organisms was known from environmental DNA sequences.[6]
Additional members of the group were isolated in 2011 by a team led by Thomas Richards, from the Natural History Museum in London, and also an evolutionary geneticist at the University of Exeter, UK. The team used DNA techniques to disclose the existence of unknown genetic material dredged from the university pond. Once they had a few unknown sequences they fluorescently labeled small DNA sequences and let them bind to the matching DNA in the whole sample (fluorescence in situ hybridization). Under fluorescence microscopy, they could see that the possessor cells were ovoid in shape and 3–5 micrometres across. They then established that the cryptomycota were present in other samples taken from further freshwater environments, soils and marine sediments.[7][8]
The common characteristic of the clade members is that they lack the chitinous cell walls present in almost all previously discovered fungi (including microsporidia) and which are a major feature of the kingdom. Without the chitin the cryptomycota can be phagotrophic parasites that feed by attaching to, engulfing, or living inside other cells. Most known fungi feed by osmotrophy—taking in nutrients from outside the cell.[7]
- ^ Karpov; et al. (2014). "Morphology, phylogeny and ecology of the aphelids (Aphelidea, Opisthokonta) and proposal for the new superphylum Opisthosporidia". Frontiers in Microbiology. 5: 112. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00112. PMC 3975115. PMID 24734027.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Jones 2011awas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Jones 2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
James 2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
van Hannen 1999was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Lara 2010was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Turner 2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ghosh 2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page).