| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
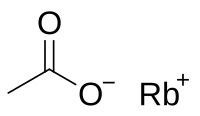
| IUPAC name
Rubidium acetate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.415 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molar mass | 144.51 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 246 °C (475 °F; 519 K) (decomposes) |
| 85 g/100 ml (45 °C)[2] | |
| log P | -0.561 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| H305, H315 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
rubidium formate |
Other cations
|
Hydrogen acetate Lithium acetate Sodium acetate Potassium acetate Caesium acetate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rubidium acetate is a rubidium salt that is the result of reacting rubidium metal, rubidium carbonate, or rubidium hydroxide with acetic acid. It is soluble in water like other acetates.[2]
- ^ "Rubidium acetate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ a b c "CXRB010_ RUBIDIUM ACETATE, monohydrate" (PDF). Retrieved 2021-02-03.
- ^ "RUBIDIUM ACETATE | 563-67-7". www.chemicalbook.com.
- ^ "Safety data sheet" (PDF). s3.amazonaws.com. 2015. Retrieved 2021-02-03.
