| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
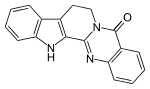
| Preferred IUPAC name
8,13-Hydroindolo[2′,3′:3,4]pyrido[2,1-b]quinazolin-5(7H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.163.752 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H13N3O | |
| Molar mass | 287.322 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rutecarpine or rutaecarpine is a COX-2 inhibitor isolated from Tetradium ruticarpum, a tree native to China.[1] It is classified as a non-basic alkaloid.[2]
In contrast to synthetic COX-2 inhibitors like etoricoxib and celecoxib, rutecarpine does not appear to cause negative effects on the cardiovascular system.[3]
- ^ Moon, T. C.; Murakami, M.; Kudo, I.; Son, K. H.; Kim, H. P.; Kang, S. S.; Chang, H. W. (1999). "A new class of COX-2 inhibitor, rutaecarpine from Evodia rutaecarpa". Inflammation Research. 48 (12): 621–625. doi:10.1007/s000110050512. PMID 10669112. S2CID 19555209.
- ^ Manske, R. H. F. (1950). "Sources of alkaloids and their isolation". In Manske, R. H. F.; Holmes, H. L. (eds.). The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Physiology. Vol. 1. Academic Press. pp. 1–14. doi:10.1016/S1876-0813(08)60184-0. ISBN 978-0-12-469501-6. S2CID 82529003.
- ^ Jia, Sujie; Hu, Changping (2010). "Pharmacological effects of rutaecarpine as a cardiovascular protective agent". Molecules. 15 (3): 1873–1881. doi:10.3390/molecules15031873. PMC 6257227. PMID 20336017. S2CID 21968872.