 | |
| Mission type | Solar science |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1965-093A |
| SATCAT no. | 1738 |
| Mission duration | 59 years and 8 days (in orbit) |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Naval Research Lab |
| Launch mass | 56.7 kilograms (125 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | November 19, 1965, 22:11:30 UTC [1][2] |
| Rocket | Scout X-4 |
| Launch site | Wallops LA-3 |
| End of mission | |
| Last contact | August 1967 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric[3] |
| Regime | Circular orbit |
| Eccentricity | 0.01302 |
| Perigee altitude | 704 kilometers (437 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 891 kilometers (554 mi) |
| Inclination | 59.7 degrees |
| Period | 100.8 minutes |
| Epoch | 19 November 1965, 04:48:00 UTC |
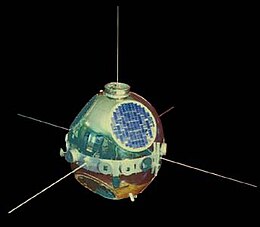
The SOLRAD 8,Explorer 30 or SE-A satellite was one of the NASA SOLRAD (Solar Radiation) program that began in 1960 to provide continuous coverage of solar radiation with a set of standard photometers. SOLRAD 8 was a spin-stabilized satellite oriented with its spin axis perpendicular to the sun-satellite line so that the 14 solar X-ray[4] and ultraviolet photometers[5] pointing radially outward from its equatorial belt viewed the sun on each revolution. Data were transmitted in real time by means of an FM / AM the satellite's telemetry system and were recorded by the stations on the Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network (STADAN) tracking network.[6]
- ^ "Solar-observing satellites". Rammb.cira.colostate.edu. Retrieved 2014-05-27.
- ^ "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Report. 21 July 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "Trajectory: Explorer 30 (Solrad 8) 1965-093A". NASA. 28 October 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ ftp://ftp.ngdc.noaa.gov/STP/SOLAR_DATA/SATELLITE_ENVIRONMENT/XRAY_BGND/docs/solrad.txt
- ^ "Solrad". Designation-systems.net. Retrieved 2014-05-27.
- ^ "Display: Explorer 30 (Solrad 8) 1965-093A". NASA. 28 October 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.