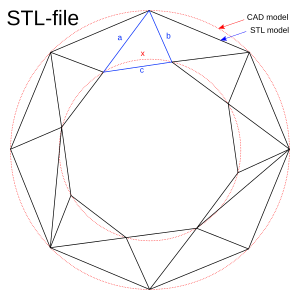
 A CAD representation of a torus (shown as two concentric red circles) and an STL approximation of the same shape (composed of triangular planes) | |
| Filename extension |
.stl |
|---|---|
| Internet media type | |
| Developed by | 3D Systems |
| Initial release | 1987 |
| Type of format | Stereolithography |
STL is a file format native to the stereolithography CAD software created by 3D Systems.[3][4][5] Chuck Hull, the inventor of stereolithography and 3D Systems’ founder, reports that the file extension is an abbreviation for stereolithography,[6] although it is also referred to as standard triangle language or standard tessellation language.[2]
An STL file describes a raw, unstructured triangulated surface by the unit normal and vertices (ordered by the right-hand rule[2]) of the triangles using a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system.[7] In the original specification, all STL coordinates were required to be positive numbers, but this restriction is no longer enforced and negative coordinates are commonly encountered in STL files today. STL files contain no scale information, and the units are arbitrary.[8] STL files describe only the surface geometry of a three-dimensional object without any representation of color, texture or other common CAD model attributes. The STL format specifies both ASCII and binary representations. Binary files are more common, since they are more compact.[9]
STL is widely used for rapid prototyping, 3D printing and computer-aided manufacturing,[10] and supported by many other software packages.[citation needed]
- ^ Noordvyk, Allan (2018-03-06). "model/stl". iana.org. IANA. Retrieved 2022-05-30.
- ^ a b c "STL (STereoLithography) File Format Family". Library of Congress. Retrieved 2022-05-30.
- ^ StereoLithography Interface Specification, 3D Systems, Inc., July 1988
- ^ StereoLithography Interface Specification, 3D Systems, Inc., October 1989
- ^ SLC File Specification, 3D Systems, Inc., 1994
- ^ Grimm, Todd (2004). "3. The Rapid Prototyping Process". User's Guide to Rapid Prototyping. Society of Manufacturing Engineers. p. 55. ISBN 0-87263-697-6.
- ^ Burkardt, John (2014-07-10). "STLA Files - ASCII stereolithography files". Retrieved 2022-05-30.
- ^ "The StL Format: Standard Data Format for Fabbers". fabbers.com — Historical resource on 3D printing. Retrieved 2022-05-30.
- ^ Burns, Marshall (1993). "6.5". Automated Fabrication: Improving Productivity in Manufacturing. Prentice Hall PTR. ISBN 9780131194625. OCLC 634954895.
- ^ Chua, C. K.; Leong, K. F.; Lim, C. S. (2003), "Chapter 6, Rapid Prototyping Formats", Rapid Prototyping: Principles and Applications (2nd ed.), World Scientific Publishing Co., p. 237, ISBN 981-238-117-1,
The STL (STeroLithography) file, as the de facto standard, has been used in many, if not all, rapid prototyping systems.