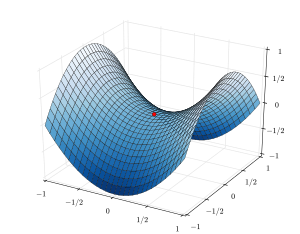
In mathematics, a saddle point or minimax point[1] is a point on the surface of the graph of a function where the slopes (derivatives) in orthogonal directions are all zero (a critical point), but which is not a local extremum of the function.[2] An example of a saddle point is when there is a critical point with a relative minimum along one axial direction (between peaks) and at a relative maximum along the crossing axis. However, a saddle point need not be in this form. For example, the function has a critical point at that is a saddle point since it is neither a relative maximum nor relative minimum, but it does not have a relative maximum or relative minimum in the -direction.

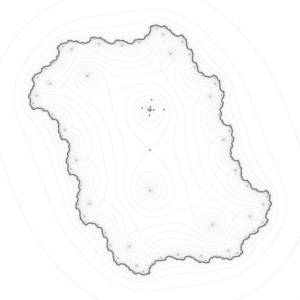
The name derives from the fact that the prototypical example in two dimensions is a surface that curves up in one direction, and curves down in a different direction, resembling a riding saddle. In terms of contour lines, a saddle point in two dimensions gives rise to a contour map with a pair of lines intersecting at the point. Such intersections are rare in actual ordnance survey maps, as the height of the saddle point is unlikely to coincide with the integer multiples used in such maps. Instead, the saddle point appears as a blank space in the middle of four sets of contour lines that approach and veer away from it. For a basic saddle point, these sets occur in pairs, with an opposing high pair and an opposing low pair positioned in orthogonal directions. The critical contour lines generally do not have to intersect orthogonally.
- ^ Howard Anton, Irl Bivens, Stephen Davis (2002): Calculus, Multivariable Version, p. 844.
- ^ Chiang, Alpha C. (1984). Fundamental Methods of Mathematical Economics (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 312. ISBN 0-07-010813-7.


