| Sahara | |
|---|---|
 The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972 | |
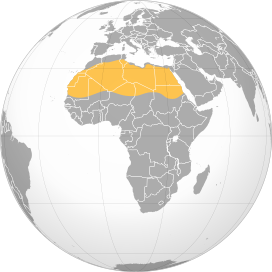 Geographical map of the Sahara | |
| Length | 4,800 km (3,000 mi) |
| Width | 1,800 km (1,100 mi) |
| Area | 9,200,000 km2 (3,600,000 sq mi) |
| Naming | |
| Native name |
|
| Geography | |
| Countries | |
| Coordinates | 23°N 13°E / 23°N 13°E |
The Sahara (/səˈhɑːrə/, /səˈhærə/) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of 9,200,000 square kilometres (3,600,000 sq mi), it is the largest hot desert in the world and the third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Arctic.[1][2][3]
The name "Sahara" is derived from Arabic: صَحَارَى, romanized: ṣaḥārā /sˤaħaːraː/, a broken plural form of ṣaḥrā' (صَحْرَاء /sˤaħraːʔ/), meaning "desert".[4][5][6][7]
The desert covers much of North Africa, excluding the fertile region on the Mediterranean Sea coast, the Atlas Mountains of the Maghreb, and the Nile Valley in Egypt and the Sudan.[8]
It stretches from the Red Sea in the east and the Mediterranean in the north to the Atlantic Ocean in the west, where the landscape gradually changes from desert to coastal plains. To the south it is bounded by the Sahel, a belt of semi-arid tropical savanna around the Niger River valley and the Sudan region of sub-Saharan Africa. The Sahara can be divided into several regions, including the western Sahara, the central Ahaggar Mountains, the Tibesti Mountains, the Aïr Mountains, the Ténéré desert, and the Libyan Desert.
For several hundred thousand years, the Sahara has alternated between desert and savanna grassland in a 20,000-year cycle[9] caused by the precession of Earth's axis (about 26,000 years) as it rotates around the Sun, which changes the location of the North African monsoon.
- ^ Cook, Kerry H.; Vizy, Edward K. (2015). "Detection and Analysis of an Amplified Warming of the Sahara Desert". Journal of Climate. 28 (16): 6560. Bibcode:2015JCli...28.6560C. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00230.1.
- ^ "Largest Desert in the World". Archived from the original on 17 August 2007. Retrieved 30 December 2011.
- ^ "Is the World Full or Empty?". Story Maps. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 19 October 2018.
- ^ "Sahara." Archived 11 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine Online Etymology Dictionary. Douglas Harper, Historian. Retrieved 25 June 2007.
- ^ "English-Arabic online dictionary". Online.ectaco.co.uk. 28 December 2006. Archived from the original on 9 March 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2010.
- ^ Wehr, Hans (1994). A Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic (Arabic-English) (4th ed.). Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz. p. 589. ISBN 978-0-87950-003-0.
- ^ al-Ba'labakkī, Rūḥī (2002). al-Mawrid: Qāmūs 'Arabī-Inklīzī (in Arabic) (16th ed.). Beirut: Dār al-'Ilm lil-Malāyīn. p. 689.
- ^ "Sahara | Location, History, Map, Countries, Animals, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ^ Chu, Jennifer (2 January 2019). "A "pacemaker" for North African climate". MIT News. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2020.