| Salinas River | |
|---|---|
 View of the Salinas River near San Ardo in May 2008. During the rainier winter months, the river may occasionally reconnect with Monterey Bay. The San Ardo Oil Field is visible in the distance. | |
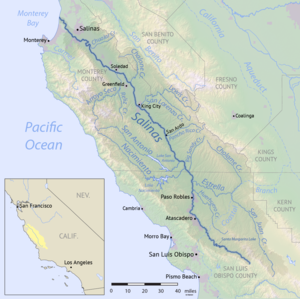 Map of the Salinas River watershed | |
| Native name | ua kot taiauačorx (Southern Ohlone) |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Cities and towns | Paso Robles, Soledad, Salinas |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Los Machos Hills in the Los Padres National Forest |
| • location | San Luis Obispo County, California |
| • coordinates | 35°12′57.2394″N 120°13′26.112″W / 35.215899833°N 120.22392000°W[3] |
| • elevation | 2,150 ft (660 m) |
| Mouth | Monterey Bay |
• location | 6 miles north of Marina, California |
• coordinates | 36°44′58″N 121°48′13″W / 36.74944°N 121.80361°W[3] |
• elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Length | 175 mi (282 km)[5] |
| Basin size | 4,160 sq mi (10,800 km2) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | near Spreckels |
| • average | 421 cu ft/s (11.9 m3/s) |
| • minimum | 0 cu ft/s (0 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 95,000 cu ft/s (2,700 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Nacimiento River, San Antonio River, Arroyo Seco |
| • right | Estrella River, San Lorenzo Creek |
The Salinas River (Rumsen: ua kot taiauačorx)[6] is the longest river of the Central Coast region of California, running 175 miles (282 km) and draining 4,160 square miles (10,800 km2).[7] It flows north-northwest and drains the Salinas Valley that slices through the central California Coast Ranges south of Monterey Bay.[3] The river begins in southern San Luis Obispo County, originating in the Los Machos Hills of the Los Padres National Forest. From there, the river flows north into Monterey County, eventually making its way to connect with the Monterey Bay, part of the Pacific Ocean, approximately 5 miles (8.0 km) south of Moss Landing. The river is a wildlife corridor, and provides the principal source of water from its reservoirs and tributaries for the farms and vineyards of the valley.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Guddewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Hoover, Mildred; et al. (1966). Historic Spots in California (3rd ed.). Palo Alto, California: Stanford University Press. p. 219.
- ^ a b c d U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Salinas River
- ^ Bancroft, Hubert H. (1884–1890). History of California. 7 vols. San Francisco, California: A.L. Bancroft and Company. p. v1/p150.
- ^ Measured in Google Earth using the path measure tool
- ^ Heizer, R.F. (5 December 1952). "The mission Indian vocabularies of Alphonse Pinart" (PDF). University of California Anthropological Records. 15 (1): 1–84. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ Donald J. Funk, Adriana Morales (2002–2003). Upper Salinas River and Tributaries Watershed Fisheries Report and Early Actions (PDF) (Report). Upper Salinas Tablas Resource Conservation District. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 July 2011. Retrieved 15 December 2010.