
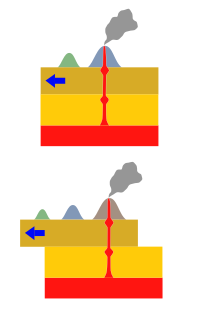
The Samoa hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located in the south Pacific Ocean. The hotspot model describes a hot upwelling plume of magma through the Earth's crust as an explanation of how volcanic islands are formed. The hotspot idea came from J. Tuzo Wilson in 1963 based on the Hawaiian Islands volcanic chain.
In theory, the Samoa hotspot is based on the Pacific Tectonic Plate travelling over a fixed hotspot located deep underneath the Samoan Islands.[1][2] The Samoa hotspot includes the Samoan Islands (American Samoa and Samoa), and extends to the islands of Uvea or Wallis Island (Wallis and Futuna) and Niulakita (Tuvalu), as well as the submerged Pasco banks and Alexa Bank.[3]
As the Pacific Plate moves slowly over the hotspot, thermal activity builds up and is released in magma plume spewing through the Earth's crust, forming each island in a chain. The Samoa islands generally lie in a straight line, east to west, in the same direction of the tectonic plate 'drifting' over the hotspot.[4]

- ^ Russell, Jamie A. "Hotspot Lesson: Samoan Hotspot". Enduring Resources Earth Science Education. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- ^ Jackson et al. 2010, Section:1 Introduction
- ^ "Samoan Hotspot Trail". Archived from the original on December 23, 2010. Retrieved 2009-12-01.
- ^ "This volcano we live on". Natural History Guide to American Samoa. Retrieved 2 December 2009.