San Francisco Bay Area | |
|---|---|
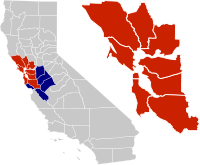 Location of the Bay Area within California. The nine-county Bay Area. Additional counties in the larger thirteen-county combined statistical area. | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Subregions | |
| Counties | |
| Core cities | Oakland San Francisco San Jose |
| Other municipalities | |
| Area | |
| • Nine-county | 6,966 sq mi (18,040 km2) |
| • San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland (CSA) | 10,191 sq mi (26,390 km2) |
| Highest elevation | 4,360 ft (1,330 m) |
| Lowest elevation | −13 ft (−4 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Density | 1,100/sq mi (430/km2) |
| • Nine-county | 7.76 million[4] |
| • San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland (CSA) | 9.22 million[4] |
| GDP | |
| • Nine-county | $1.132 trillion (2022) |
| • San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland (CSA) | $1.383 trillion (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC−08:00 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) |
| Area codes | 408/669, 415/628, 510/341, 650, 707, 925[7] |
| Website | bayareametro |
The San Francisco Bay Area, commonly known as the Bay Area, is a region of California surrounding and including San Francisco Bay.[8] The Association of Bay Area Governments defines the Bay Area as including the nine counties that border the estuaries of San Francisco Bay, San Pablo Bay, and Suisun Bay: Alameda, Contra Costa, Marin, Napa, San Mateo, Santa Clara, Solano, Sonoma, and San Francisco. Other definitions may be either smaller or larger, and may include neighboring counties which are not officially part of the San Francisco Bay Area, such as the Central Coast counties of Santa Cruz, San Benito, and Monterey, or the Central Valley counties of San Joaquin, Merced, and Stanislaus.[9] The Bay Area is known for its natural beauty, prominent universities, technology companies, and affluence. The Bay Area contains many cities, towns, airports, and associated regional, state, and national parks, connected by a complex multimodal transportation network.
The earliest archaeological evidence of human settlements in the Bay Area dates back to 8000–10,000 BC. The oral tradition of the Ohlone and Miwok people suggests they have been living in the Bay Area for several hundreds if not thousands of years.[10][11] The Spanish empire claimed the area beginning in the early period of Spanish colonization of the Americas. The earliest Spanish exploration of the Bay Area took place in 1769. The Mexican government controlled the area from 1821 until the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. Also in 1848, James W. Marshall discovered gold in nearby mountains, resulting in explosive immigration to the area and the precipitous decline of the Native population. The California Gold Rush brought rapid growth to San Francisco.[12] California was admitted as the 31st state in 1850. A major earthquake and fire leveled much of San Francisco in 1906. During World War II, the Bay Area played a major role in America's war effort in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater, with the San Francisco Port of Embarkation, of which Fort Mason was one of 14 installations and location of the headquarters, acting as a primary embarkation point for American forces. Since then, the Bay Area has experienced numerous political, cultural, and artistic movements, developing unique local genres in music and art and establishing itself as a hotbed of progressive politics. Economically, the post-war Bay Area saw large growth in the financial and technology industries, creating an economy with a gross domestic product of over $700 billion. In 2018 it was home to the third-highest concentration of Fortune 500 companies in the United States.[13][14]
The Bay Area is home to approximately 7.52 million people.[15] The larger federal classification, the combined statistical area of the region which includes 13 counties,[9] is the second-largest in California—after the Greater Los Angeles area—and the fifth-largest in the United States, with over 9 million people.[16] The Bay Area's population is ethnically diverse: roughly three-fifths of the region's residents are Hispanic/Latino, Asian, African/Black, Indian, or Pacific Islander, all of whom have a significant presence throughout the region. Most of the remaining two-fifths of the population is non-Hispanic White American. The most populous cities of the Bay Area are San Francisco, Oakland, and San Jose, the latter of which had a population of 969,655 in 2023, making San Jose the area's largest city and the 13th-most populous in the United States.[17][18]
Despite its urban character, San Francisco Bay is one of California's most ecologically sensitive habitats, providing important ecosystem services such as filtering the pollutants and sediments from rivers and supporting a number of endangered species. In addition, the Bay Area is known for its stands of coast redwoods, many of which are protected in state and county parks. The region is additionally known for the complexity of its landforms, the result of millions of years of tectonic plate movements. Because the Bay Area is crossed by six major earthquake faults, the region is particularly exposed to hazards presented by large earthquakes. The climate is temperate and conducive to outdoor recreational and athletic activities such as hiking, running, and cycling. The Bay Area is host to five professional sports teams and is a cultural center for music, theater, and the arts. It is also host to numerous higher education institutions, including research universities such as the University of California, Berkeley, and Stanford University, the latter known for helping to create the high tech center called Silicon Valley. Home to 101 municipalities and 9 counties, governance in the Bay Area involves numerous local and regional jurisdictions, often with broad and overlapping responsibilities.
- ^ "Square Mileage by County". California States Association of Counties. Archived from the original on February 27, 2019. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ Hinrichs, Scott (September 28, 2006). "Mt. Hamilton Lick Observatory". Milpitas Camera Club. Archived from the original on August 20, 2010. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ Kurhi, Eric (December 11, 2014). "San Jose: Overwhelmed pumps led to Alviso flooding; residents say it's a 'wake-up call'". San Jose Mercury News. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ a b "2020 Population and Housing State Data". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ^ "GDP by county in 2022" (PDF). www.unc.edu.
- ^ "Gross Domestic Product by County and Metropolitan Area", Federal Reserve Economic Data, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
- ^ "Area Code Map for Northern California/Bay Area". White Pages. Archived from the original on September 24, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- ^ Scott, Mel (1985). The San Francisco Bay Area: A Metropolis in Perspective (2 ed.). University of California Press. p. ix. ISBN 9780520055124.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
OMB-23-01was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:54was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:64was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "IPUMS NHGIS | National Historical Geographic Information System". www.nhgis.org. Retrieved December 8, 2023.
- ^ "Home". Bay Area Council. Archived from the original on August 31, 2019. Retrieved September 7, 2019.
- ^ "2019 Sacramento Economic Forecast" (PDF). Bay Area Council. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 26, 2019.
- ^ "It's Official: A Quarter Million People Fled the Bay Area Since 2020". The San Francisco Standard. March 31, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ "Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas Population Totals: 2020-2022". Census.gov. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on August 7, 2022. Retrieved December 3, 2019.
- ^ "San Jose no longer in Top 10 of most populous U.S. cities". The Mercury News. May 18, 2023. Retrieved May 20, 2023.






