| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
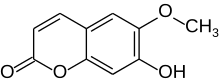
| Preferred IUPAC name
7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one | |
| Other names
7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one
7-Hydroxy-6-methoxychromen-2-one Gelseminic acid Chrysatropic acid Scopoletine 6-Methylesculetin Murrayetin Scopoletol Escopoletin Methylesculetin 6-O-Methylesculetin Esculetin-6-methyl ether 7-Hydroxy-5-methoxycoumarin 6-Methoxyumbelliferone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.975 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 192.16 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Scopoletin is a coumarin found in the root of plants in the genus Scopolia such as Scopolia carniolica and Scopolia japonica, in chicory, in Artemisia scoparia, in the roots and leaves of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica), in the passion flower, in Brunfelsia, in Viburnum prunifolium, in Solanum nigrum,[1] in Datura metel,[2] in Mallotus resinosus,[3] or and in Kleinhovia hospita. It can also be found in fenugreek,[4] vinegar,[5][4] some whiskies or in dandelion coffee. A similar coumarin is scoparone. Scopoletin is highly fluorescent when dissolved in DMSO or water and is regularly used as a fluorimetric assay for the detection of hydrogen peroxide in conjunction with horseradish peroxidase. When oxidized, its fluorescence is strongly suppressed.
- ^ Zhao Y; Liu F; Lou HX (2010). "[Studies on the chemical constituents of Solanum nigrum]". Zhong Yao Cai (in Chinese). 33 (4): 555–556. PMID 20845784.
- ^ Han XL, Wang H, Zhang ZH, Tan Y, Wang JH (August 2015). "[Study on Chemical Constituents in Seeds of Datura metel from Xinjiang]". Zhong Yao Cai = Zhongyaocai = Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials (in Chinese). 38 (8): 1646–8. PMID 26983236.
- ^ Ma J; Jones SH; Hecht SM (2004). "A coumarin from Mallotus resinosus that mediates DNA cleavage". J Nat Prod. 67 (9): 1614–1616. doi:10.1021/np040129c. PMID 15387675.
- ^ a b Ouzir, M; El Bairi, K; Amzazi, S (October 2016). "Toxicological properties of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum)". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 96: 145–54. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2016.08.003. PMID 27498339.
- ^ Analysis of polyphenolic compounds of different vinegar samples. Miguel Carrero Gálvez, Carmelo García Barroso and Juan Antonio Pérez-Bustamante, Zeitschrift für Lebensmitteluntersuhung und -Forschung A, Volume 199, Number 1, pages 29-31, doi:10.1007/BF01192948