| second | |
|---|---|
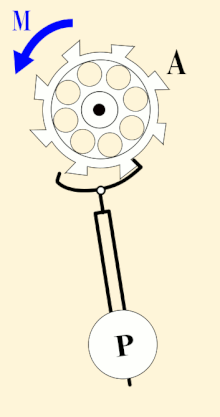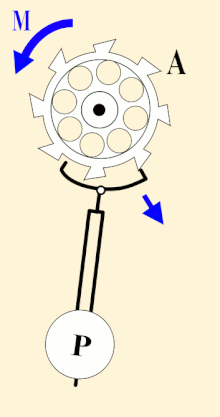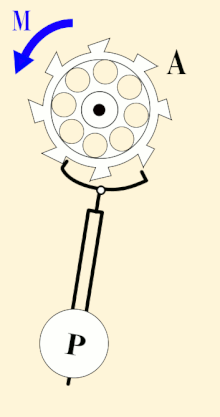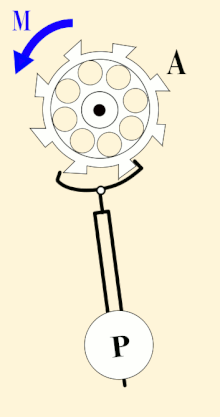 A pendulum-governed escapement of a clock, ticking every second | |
| General information | |
| Unit system | SI |
| Unit of | time |
| Symbol | s |
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time, historically defined as 1⁄86400 of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400).
The current and formal definition in the International System of Units (SI) is more precise:
The second [...] is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, ΔνCs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be 9192631770 when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1.[1]
This current definition was adopted in 1967 when it became feasible to define the second based on fundamental properties of nature with caesium clocks.[2] Because the speed of Earth's rotation varies and is slowing ever so slightly, a leap second is added at irregular intervals to civil time[nb 1] to keep clocks in sync with Earth's rotation.
- ^ "SI Brochure (2019)" (PDF). SI Brochure. BIPM. p. 130. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 23, 2019. Retrieved May 23, 2019.
- ^ Gill, Patrick (October 28, 2011). "When should we change the definition of the second?". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 369 (1953): 4109–4130. Bibcode:2011RSPTA.369.4109G. doi:10.1098/rsta.2011.0237. PMID 21930568. S2CID 6896025.
Cite error: There are <ref group=nb> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=nb}} template (see the help page).