The sectoral balances (also called sectoral financial balances) are a sectoral analysis framework for macroeconomic analysis of national economies developed by British economist Wynne Godley.[1]
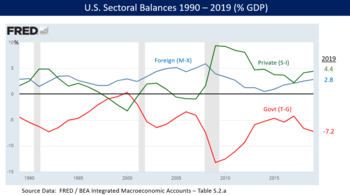
Sectoral analysis is based on the insight that when the government sector has a budget deficit, the non-government sectors (private domestic sector and foreign sector) together must have a surplus, and vice versa. In other words, if the government sector is borrowing, the other sectors taken together must be lending. The balances represent an accounting identity resulting from rearranging the components of aggregate demand, showing how the flow of funds affects the financial balances of the three sectors.[4][5]
This corresponds approximately to Balances Mechanics developed by Wolfgang Stützel in the 1950s. The approach is used by scholars at the Levy Economics Institute to support macroeconomic modelling and by Modern Monetary Theorists to illustrate the relationship between government budget deficits and private saving.[4][5]
- ^ Goldman's Top Economist Explains The World's Most Important Chart, And His Big Call For The US Economy
- ^ New Policy Institute-United States Sectoral Balances over Five Decades-July 29, 2011
- ^ FRED-Sectoral Balances Three Line Annual-Retrieved September 7, 2020
- ^ a b Fiebeger, Brett (2013). "A constructive critique of the Levy Sectoral Financial Balance approach". Real World Economics Review: 59–80.
- ^ a b Bloomberg-Coy, Dmitrieva & Boesler-A Beginner's Guide to MMT-March 21, 2019