 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Revolution, Stronghold, Revolt |
| Other names | 25-cyclohexyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-5-deoxy-22,23-dihydro-5-(hydroxyimino)-avermectin B1 monosaccharide[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.250.168 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
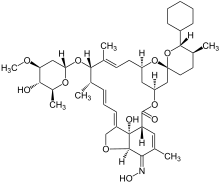
| Formula | C43H63NO11 |
| Molar mass | 769.973 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Selamectin, sold under the brand name Revolution, among others, is a topical parasiticide and anthelminthic used on dogs and cats.[2] It treats and prevents infections of heartworms, fleas, ear mites, sarcoptic mange (scabies), and certain types of ticks in dogs, and prevents heartworms, fleas, ear mites, hookworms, and roundworms in cats.[citation needed] It is structurally related to ivermectin and milbemycin.[citation needed] Selamectin is not approved for human use.[citation needed]
- ^ Bishop BF, Bruce CI, Evans NA, Goudie AC, Gration KA, Gibson SP, et al. (August 2000). "Selamectin: a novel broad-spectrum endectocide for dogs and cats". Veterinary Parasitology. 91 (3–4): 163–176. doi:10.1016/s0304-4017(00)00289-2. PMID 10940519.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - ^ a b "Revolution- selamectin solution". DailyMed. 1 December 2023. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ "Evicto EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 1 August 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ "Stronghold EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 25 March 2008. Retrieved 29 June 2024.