This article provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject. (June 2020) |

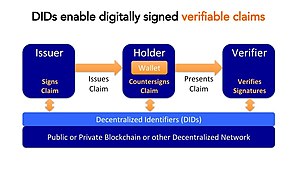
Self-sovereign identity (SSI) is an approach to digital identity that gives individuals control over the information they use to prove who they are to websites, services, and applications across the web. Without SSI, individuals with persistent accounts (identities) across the internet must rely on a number of large identity providers, such as Facebook (Facebook Connect) and Google (Google Sign-In), that have control of the information associated with their identity.[2][3][4] If a user chooses not to use a large identity provider, then they have to create new accounts with each service provider, which fragments their web experiences. Self-sovereign identity offers a way to avoid these two undesirable alternatives. In a self-sovereign identity system, the user accesses services in a streamlined and secure manner, while maintaining control over the information associated with their identity.[5][6]
- ^ "Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)". World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved 15 July 2020.
- ^ Chaffer, Tomer Jordi; Goldston, Justin (November 2022). "On the Existential Basis of Self-Sovereign Identity and Soulbound Tokens: An Examination of the "Self" in the Age of Web3". Journal of Strategic Innovation and Sustainability. Retrieved July 19, 2023.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:0was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Windley, Phillip J. (2021). "Sovrin: An Identity Metasystem for Self-Sovereign Identity". Frontiers in Blockchain. 4. doi:10.3389/fbloc.2021.626726.
- ^ "Verifiable Claims Working Group Frequently Asked Questions". World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). 12 August 2022. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- ^ Ferdous, Md Sadek; Chowdhury, Farida; Alassafi, Madini O. (2019). "In Search of Self-Sovereign Identity Leveraging Blockchain Technology". IEEE Access. 7: 103059–103079. Bibcode:2019IEEEA...7j3059F. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931173. hdl:10044/1/77538. ISSN 2169-3536.