| Septo-optic dysplasia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | de Morsier syndrome[1][2] |
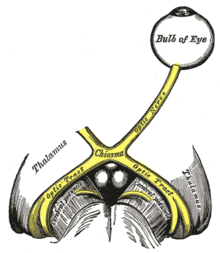 | |
| The optic nerve is underdeveloped in this condition. | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
| Diagnostic method | congenital hypopituitarism, holoprosencephaly[3] |
Septo-optic dysplasia (SOD), known also as de Morsier syndrome, is a rare congenital malformation syndrome that features a combination of the underdevelopment of the optic nerve, pituitary gland dysfunction, and absence of the septum pellucidum (a midline part of the brain). Two or more of these features need to be present for a clinical diagnosis—only 30% of patients have all three.[4] French-Swiss doctor Georges de Morsier first recognized the relation of a rudimentary or absent septum pellucidum with hypoplasia of the optic nerves and chiasm in 1956.[5]
- ^ synd/2548 at Who Named It?
- ^ de Morsier G (1956). "Études sur les dysraphies, crânioencéphaliques. III. Agénésie du septum palludicum avec malformation du tractus optique. La dysplasie septo-optique" [Studies on dysraphias, cranioencephalic. III. Agenesis of the septum palludicum with malformation of the optic tract. Septo-optic dysplasia.]. Schweizer Archiv für Neurologie und Psychiatrie (in French). 77. Zurich: 267–292.
- ^ "Septo-Optic Dysplasia Spectrum". Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD). Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ Gleason, CA; Devascar, S (5 October 2011). "Congenital malformations of the Central Nervous System". Avery's Diseases of the Newborn (9 ed.). Saunders. p. 857. ISBN 978-1437701340.
- ^ Daroff RB, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL (2015-10-25). Bradley's neurology in clinical practice (Seventh ed.). London. ISBN 9780323339162. OCLC 932031625.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)